Oncology in Turkey
Oncology is the department that deals with cancerous diseases of all sorts. The word "onco" means mass or tumor, while "-logy" means study in any area. Thus, oncology is a field that researches, diagnoses, and treats cancerous diseases. As with any medical discipline, oncology has various methods of treatment, diagnosis, and applications, both surgically and medicinally. Although modern medicine has the ability to cure cancer permanently and with great precision, cancer is still a disease that afflicts humans in the most gruesome ways, and it should be treated with sensibility and professionalism. Oncologists often consult other departments for various treatment methods and the diagnosis of the tumor(s) in question. Let’s take a deeper look into the different techniques used in the treatment of cancer and different types of diseases.
What is Cancer?
Each cell of the human body has a tightly regulated system that controls its growth, maturity, reproduction, and death. Cancer begins when cells in a part of the body begin to descend out of control as a result of genetic damage and accumulation at the cellular level. There are many types of cancerous diseases. Although, out-of-control and abnormal proliferation of cells is a common feature of all cancers.
Medical Oncology
Medical oncology is a subspecialty in which physicians specialize in oncology. To become a medical oncologist, it is necessary to specialize in internal medicine for 3 extra years. Medical oncology mainly deals with the treatment of cancer with drugs. These drugs are namely chemotherapy, hormonal treatments, smart drugs, and immunotherapies. However, medical oncologists deal with the entire cancer treatment process. Professionals who specialize in oncology are called cancer specialists or medical oncologists. A medical oncologist is a doctor who has control over the entire process of cancer. They oversee cancer prevention, cancer risk, diagnosis, treatment planning and implementation, and supportive treatments.
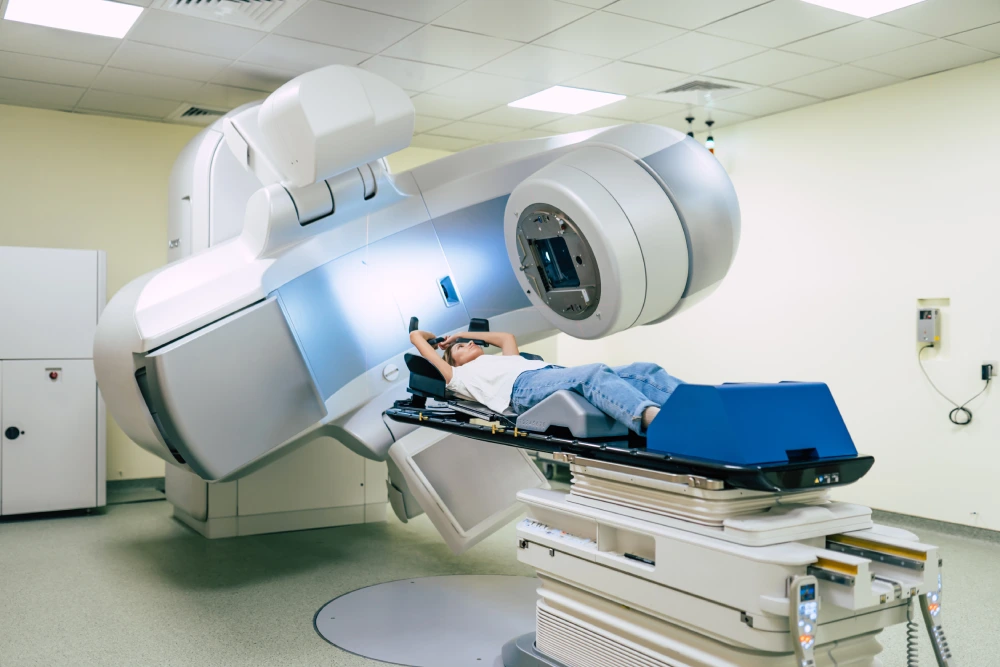
Radiation Oncology
Radiation oncology is the branch in which medical doctors specialize in basic medical training. Radiation oncology is the medical field that studies the effects of treatment procedures using radiotherapy on cancer cells.
Gynecological Oncology
Gynecological oncology is the branch of medicine that deals with cancers specific to women. Medical doctors become gynecologists by doing subspecialties in obstetrics and gynecology. Gynecological cancers include cancers of the uterus, cervix, ovary, vulva, and vagina.
Surgical Oncology
Cancer surgeries are often performed by oncological surgeons with advanced expertise in the surgery of respective cancer. In cancer surgeries, the oncological surgeon removes the tumor intact and with some normal tissue around it (this is called clear surgical margins or negative surgical margins). However, the lymph nodes closest to the cancer are also often removed to detect possible cancerous cancer cells.
Pediatric Oncology
Pediatric oncology is the branch of oncology that deals with infants who get afflicted with cancer. It is often referred to as pediatric hematooncology. The most common childhood cancers are leukemia, central nervous system tumors, lymphoma, soft tissue sarcomas, neuroblastoma, kidney cancer, bone cancer, germ cell cancers, and retinoblastoma.
How Does Oncology Diagnose Cancer?
The most important diagnostic tool remains the clinical history of the patient. Common signs of cancer include fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, palpable masses, new onset, and worsening complaints. To diagnose possible cancer, taking a tissue sample (biopsy) from a tumor suspected of cancer and examining this tissue sample under a microscope is vital. Biopsy and pathological evaluation are indispensable in oncology. Gastrointestinal systems are examined with endoscopy procedures. Ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) is also applied for the scanning and diagnosis.
What are the Subfields of Oncology?
Medical oncologist, hematologist, oncological surgeon, nuclear medicine specialist, radiologist and interventional radiologist, radiation oncologist, pathologist, molecular pathologist, geneticist, infectious diseases specialist, palliative care specialist, psycho-oncologist, complementary and alternative medicine specialist, training nurses are among many of the professionals who work together and in coordination to diagnose, examine and treat cancer.
What are the Concepts of Relapse and Remission?
The reappearance of cancer after initial treatment is completed is called a recurrence or relapse. The disappearance of all signs of the disease after treatment is called remission. If cancer recurs, detecting it early and following the patient in remission are among the important duties of oncologists.